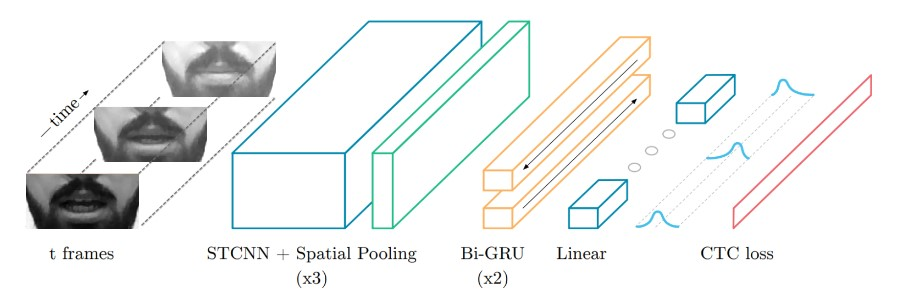
Enhancing Sentiment Classification on Small Datasets through Data Augmentation and Transfer Learning
Small-scale sentiment classification suffers from data scarcity, which limits model generalization. This study systematically compares three text augmentation strategies under a controlled, reproducible framework.
- EDA (Easy Data Augmentation) based on token-level synonym replacement, insertion, deletion, and swapping.
- Back-translation using English↔French MarianMT models to create high-fidelity paraphrases.
- Contextual token substitution (NLPaug-style) with pre-trained language models for semantics-preserving edits.
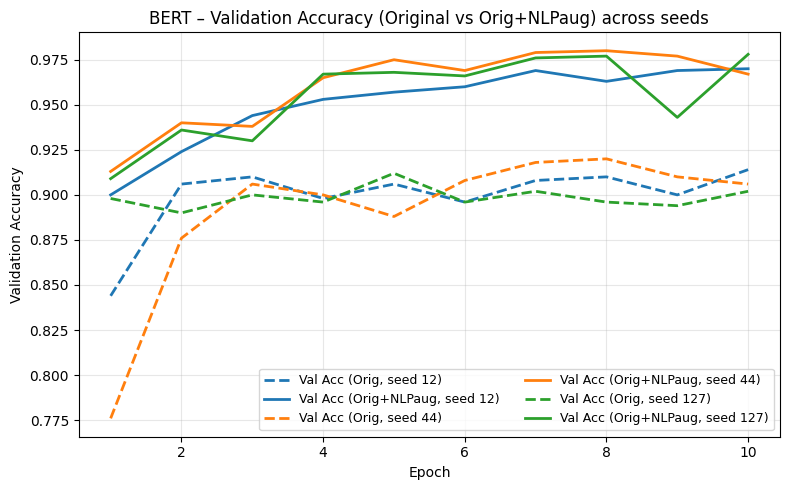
Methods: Experiments use a 5,000-sample IMDb subset with 100% augmentation, 10-fold cross-validation, and fixed seeds, comparing traditional classifiers (Logistic Regression, Random Forest) and a fine-tuned BERT base model on accuracy, F1, AUC, and effect sizes.
- All augmentation strategies yield significant and statistically robust performance gains over non-augmented baselines.
- Contextual augmentation delivers the most consistent improvements for BERT, reaching about 97% test accuracy on the augmented setting.
- EDA and back-translation provide larger relative gains for traditional models, especially Random Forest, while exhibiting different diversity–cost trade-offs.